Hi, there 👋
I am currently a Ph.D student in Nankai University from August 2022, supervised by Prof. Yaxing Wang. I obtained my master’s degree in Computer Technology from the College of Computer Science, Nankai University.
My research interests include Generative Models, Image Generation, and Image-to-image Translation.
I’m currently conducting some research in image editing and efficient inference, including:
🎨 Image editing based on Generative Models (GANs and Diffusion Models).
🚀 The acceleration of inferecne by training-free or data-free distillation.
I am currently on the job market and looking for full-time positions and postdoctoral positions. Please contact me via email if you know of any opportunities.
🔥 News
- [2025.09] 🥳🥳 Two papers (SADis and Cradle2Cane) accepted by NeurIPS2025. (NeurIPS2025 Top Reviewer)
- [2025.02] 🥳🥳 Two papers (including one co-authored paper MaskUNet) accepted by CVPR2025.
✨One-Way Ticket : Time-Independent Unified Encoder for Distilling Text-to-Image Diffusion Model. See paper and Github.
- [2025.01] 🥳🥳 Two papers (including one co-authored Spotlight paper 1Prompt1Story) accepted by ICLR2025.
✨InterLCM: Low-Quality Images as Intermediate States of Latent Consistency Models for Effective Blind Face Restoration. See paper and Project Page.
- [2024.09] 🥳🥳 StyleDiffusion: Prompt-Embedding Inversion for Text-Based Editing accepted by CVMJ2024. See paper and code.
- [2024.09] 🥳🥳 Faster Diffusion: Rethinking the Role of the Encoder for Diffusion Model Inference accepted by NeurIPS2024. See paper and Project Page.
- [2024.01] 🥳🥳 Get What You Want, Not What You Don’t: Image Content Suppression for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models accepted by ICLR2024. See paper and code.
- [2023.12] 🎉🎉 New work Faster Diffusion: Rethinking the Role of UNet Encoder in Diffusion Models. See paper and code.
- [2023.02] 🥳🥳 3D-Aware Multi-Class Image-to-Image Translation with NeRFs accepted by CVPR2023. See paper and code.
- [2020.12] 🥳🥳 Low-rank Constrained Super-Resolution for Mixed-Resolution Multiview Video accepted by TIP2020. See paper and code.
📝 Publications
CVPR 2025
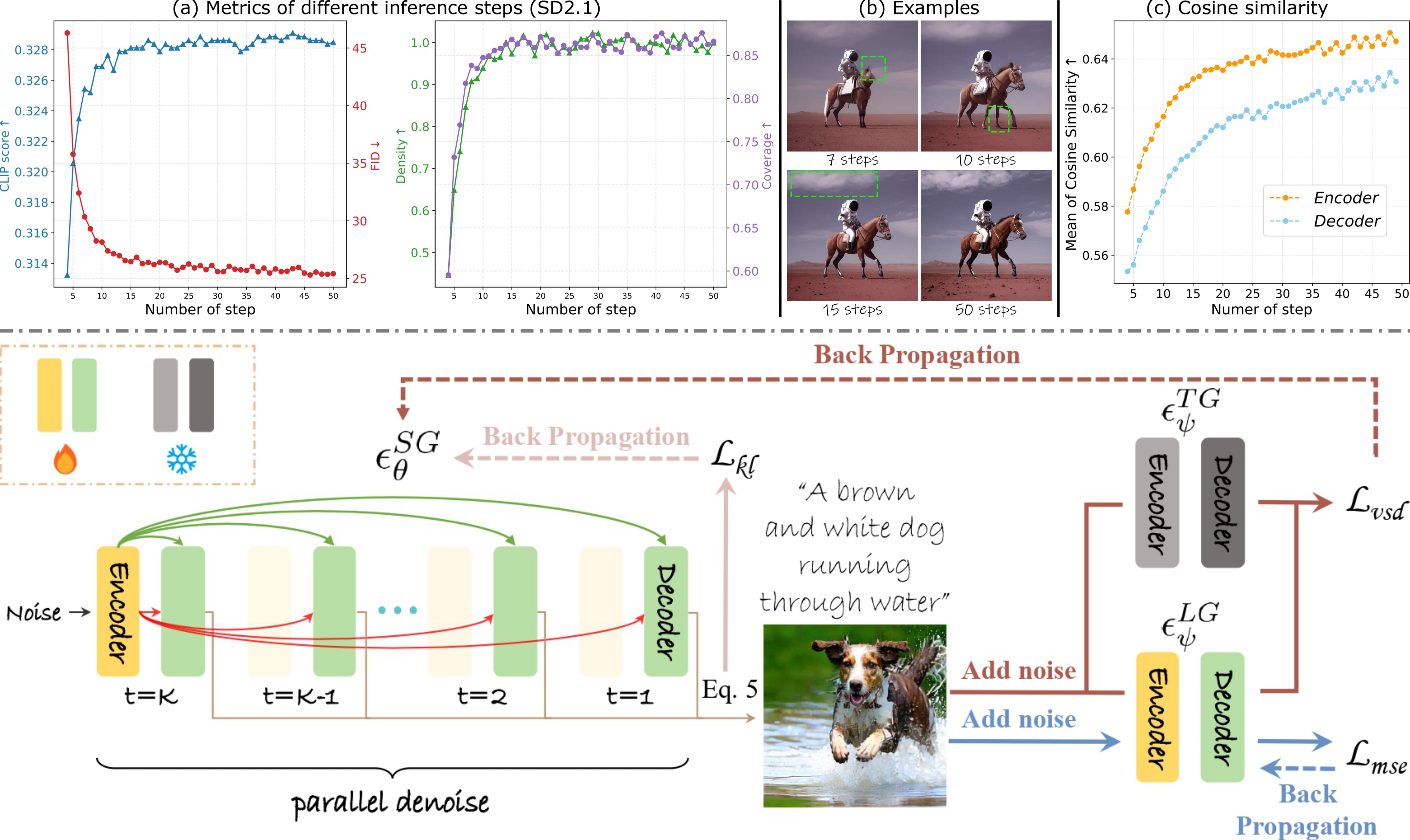
One-Way Ticket : Time-Independent Unified Encoder for Distilling Text-to-Image Diffusion Model
Senmao Li, Lei Wang, Kai Wang, Tao Liu, Jiehang Xie, Joost van de Weijier, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Shiqi Yang, Yaxing Wang*, Jian Yang
- We introduce the first Time-independent Unified Encoder (TiUE) architecture, which is a loop-free distillation approach and eliminates the need for iterative noisy latent processing while maintaining high sampling fidelity with a time cost comparable to previous one-step methods.
[paper]|
[中译版]
[code]
[abstract]
Text-to-Image (T2I) diffusion models have made remarkable advancements in generative modeling; however,
they face a trade-off between inference speed and image quality, posing challenges for efficient deployment.
Existing distilled T2I models can generate high-fidelity images with fewer sampling steps, but often struggle with diversity and quality, especially in one-step models.
From our analysis, we observe redundant computations in the UNet encoders.
Our findings suggest that, for T2I diffusion models, decoders are more adept at capturing richer and more explicit semantic information,
while encoders can be effectively shared across decoders from diverse time steps.
Based on these observations, we introduce the first Time-independent Unified Encoder (TiUE) for the student model UNet architecture,
which is a loop-free image generation approach for distilling T2I diffusion models. Using a one-pass scheme,
TiUE shares encoder features across multiple decoder time steps, enabling parallel sampling and significantly reducing inference time complexity.
In addition, we incorporate a KL divergence term to regularize noise prediction, which enhances the perceptual realism and diversity of the generated images.
Experimental results demonstrate that TiUE outperforms state-of-the-art methods, including LCM, SD-Turbo, and SwiftBrushv2, producing more diverse and realistic results while maintaining the computational efficiency.
[slide]
[poster]
ICLR 2025
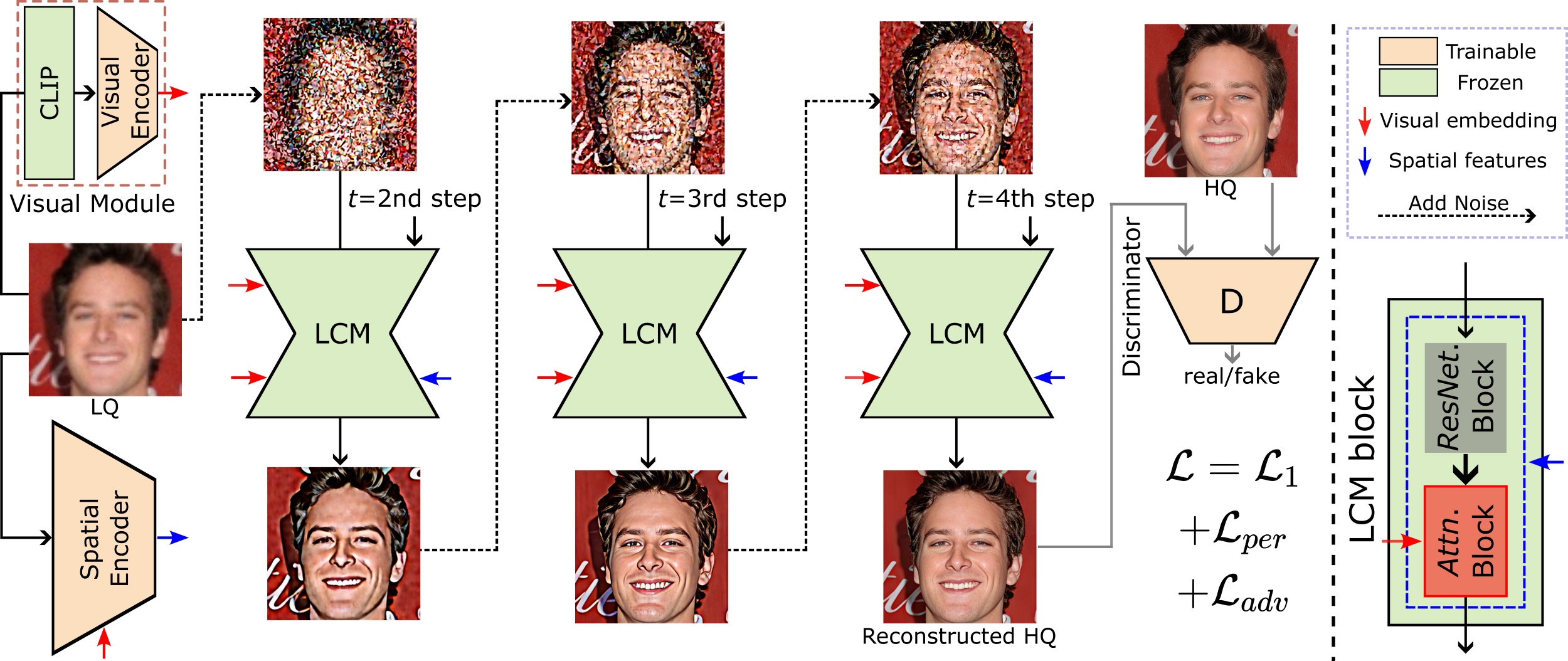
InterLCM: Low-Quality Images as Intermediate States of Latent Consistency Models for Effective Blind Face Restoration
Senmao Li, Kai Wang*, Joost van de Weijier, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Chun-Le Guo, Shiqi Yang, Yaxing Wang, Jian Yang, Ming-Ming Cheng
- By considering the low-quality image as the intermediate state of LCM models, we can effectively maintain better semantic consistency in face restorations.
- Our method InterLCM has additional advantages: few-step sampling with much faster speed and integrating our framework with commonly used perceptual loss and adversarial loss in face restoration.
[paper]|
[中译版]
[code]
[abstract]
Diffusion priors have been used for blind face restoration (BFR) by fine-tuning diffusion models (DMs) on restoration datasets to recover low-quality images. However, the naive application of DMs presents several key limitations.
(i) The diffusion prior has inferior semantic consistency (e.g., ID, structure and color.), increasing the difficulty of optimizing the BFR model;
(ii) reliance on hundreds of denoising iterations, preventing the effective cooperation with perceptual losses, which is crucial for faithful restoration.
Observing that the latent consistency model (LCM) learns consistency noise-to-data mappings on the ODE-trajectory and therefore shows more semantic consistency in the subject identity, structural information and color preservation,
we propose InterLCM to leverage the LCM for its superior semantic consistency and efficiency to counter the above issues.
Treating low-quality images as the intermediate state of LCM, InterLCM achieves a balance between fidelity and quality by starting from earlier LCM steps.
LCM also allows the integration of perceptual loss during training, leading to improved restoration quality, particularly in real-world scenarios.
To mitigate structural and semantic uncertainties, InterLCM incorporates a Visual Module to extract visual features and a Spatial Encoder to capture spatial details, enhancing the fidelity of restored images.
Extensive experiments demonstrate that InterLCM outperforms existing approaches in both synthetic and real-world datasets while also achieving faster inference speed.
[poster]
[demo]
NeurIPS 2024
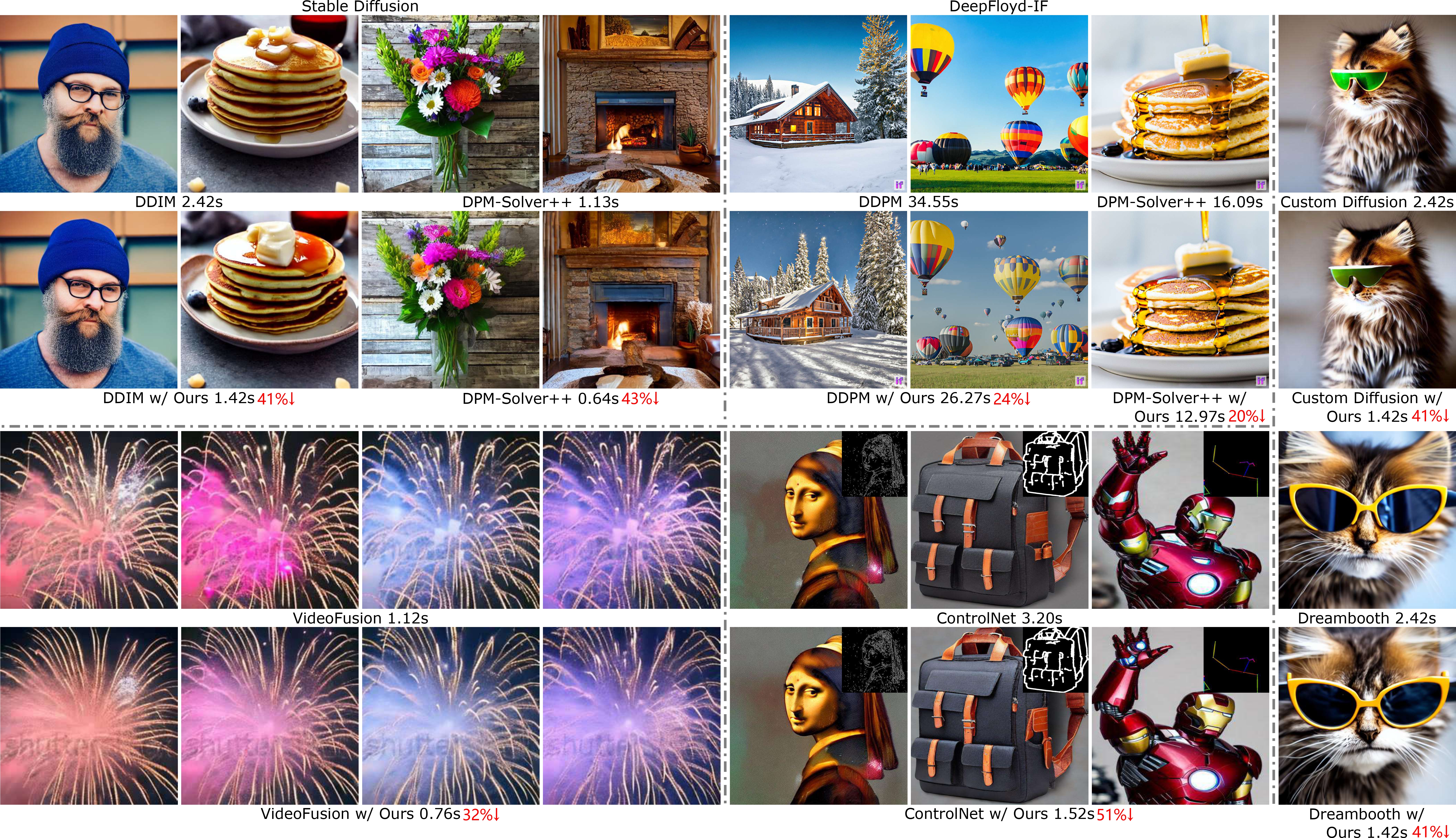
Faster Diffusion: Rethinking the Role of the Encoder for Diffusion Model Inference
Senmao Li, Taihang Hu, Joost van de Weijier, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Linxuan Li, Shiqi Yang, Yaxing Wang*, Ming-Ming Cheng, Jian Yang
- A thorough empirical study of the features of the UNet in the diffusion model showing that encoder features vary minimally (whereas decoder feature vary significantly)
- An encoder propagation scheme to accelerate the diffusion sampling without requiring any training or fine-tuning technique
- ~1.8x acceleration for stable diffusion, 50 DDIM steps, ~1.8x acceleration for stable diffusion, 20 Dpm-solver++ steps, and ~1.3x acceleration for DeepFloyd-IF
[paper]|
[中译版]
[code]
[abstract]
One of the key components within diffusion models is the UNet for noise prediction. While several works have explored basic properties of the UNet decoder, its encoder largely remains unexplored. In this work, we conduct the first comprehensive study of the UNet encoder. We empirically analyze the encoder features and provide insights to important questions regarding their changes at the inference process. In particular, we find that encoder features change gently, whereas the decoder features exhibit substantial variations across different time-steps. This finding inspired us to omit the encoder at certain adjacent time-steps and reuse cyclically the encoder features in the previous time-steps for the decoder. Further based on this observation, we introduce a simple yet effective encoder propagation scheme to accelerate the diffusion sampling for a diverse set of tasks. By benefiting from our propagation scheme, we are able to perform in parallel the decoder at certain adjacent time-steps. Additionally, we introduce a prior noise injection method to improve the texture details in the generated image. Besides the standard text-to-image task, we also validate our approach on other tasks: text-to-video, personalized generation and reference-guided generation. Without utilizing any knowledge distillation technique, our approach accelerates both the Stable Diffusion (SD) and the DeepFloyd-IF models sampling by 41% and 24% respectively, while maintaining high-quality generation performance.
[slide]
[poster]
[中文解读]
ICLR 2024
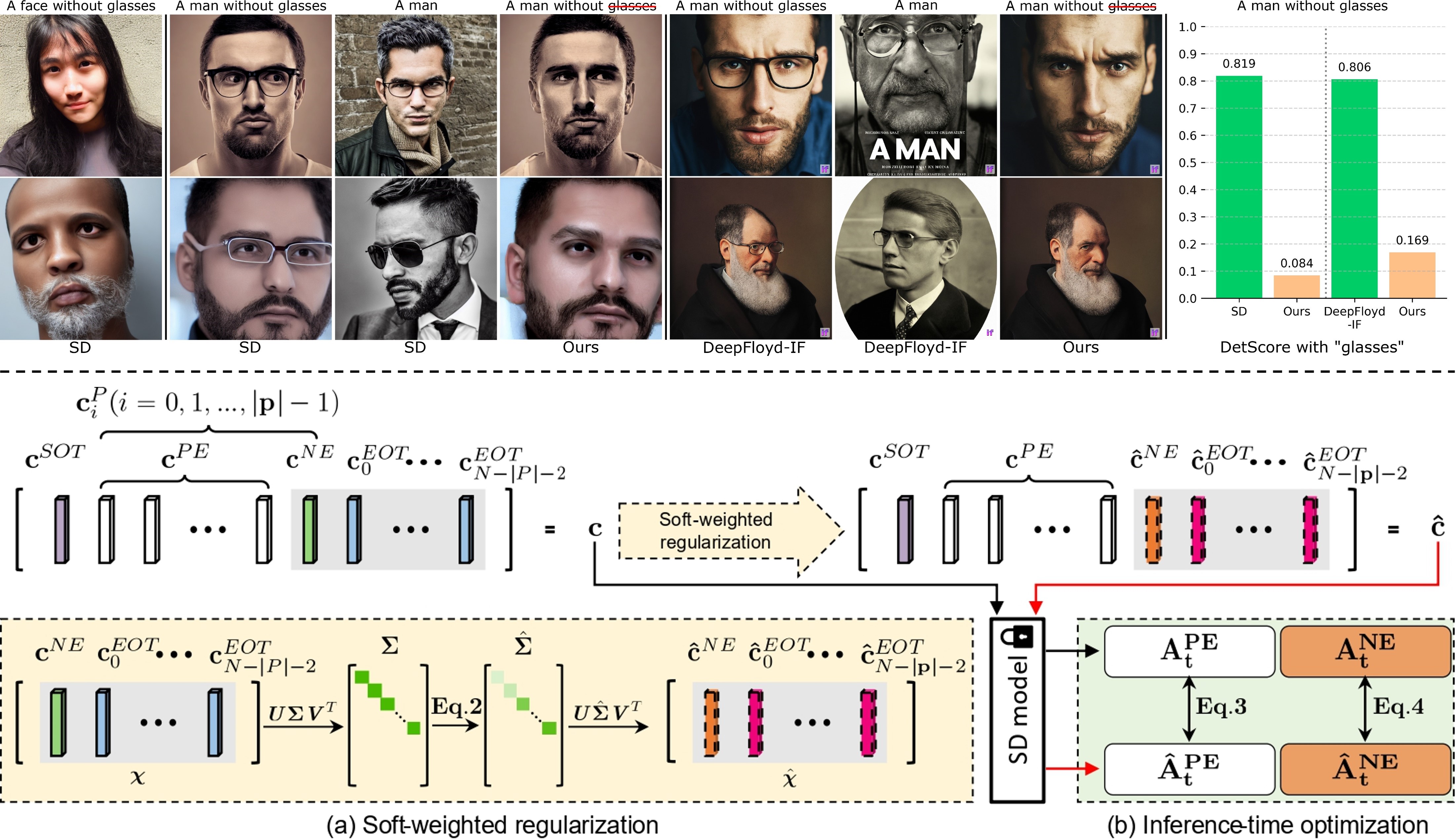
Get What You Want, Not What You Don’t: Image Content Suppression for Text-to-Image Diffusion Model
Senmao Li, Joost van de Weijer, Taihang Hu, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Qibin Hou, Yaxing Wang*, Jian Yang
- The [EOT] embeddings contain significant, redundant and duplicated semantic information of the whole input prompt.
- We propose soft-weighted regularization (SWR) to eliminate the negative target information from the [EOT] embeddings.
- We propose inference-time text embedding optimization (ITO).
[paper]|
[中译版]
[code]
[abstract]
The success of recent text-to-image diffusion models is largely due to their capacity to be guided by a complex text prompt, which enables users to precisely describe the desired content. However, these models struggle to effectively suppress the generation of undesired content, which is explicitly requested to be omitted from the generated image in the prompt. In this paper, we analyze how to manipulate the text embeddings and remove unwanted content from them. We introduce two approaches, which we refer to as **soft-weighted regularization** and **inference-time text embedding optimization**. The first regularizes the text embedding matrix and effectively suppresses the undesired content. The second method aims to further suppress the unwanted content generation of the prompt, and encourages the generation of desired content. We evaluate our method quantitatively and qualitatively on extensive experiments, validating its effectiveness. Furthermore, our method is generalizability to both the pixel-space diffusion models (i.e. DeepFloyd-IF) and the latent-space diffusion models (i.e. Stable Diffusion).
[poster]
[中文解读]
CVMJ 2024
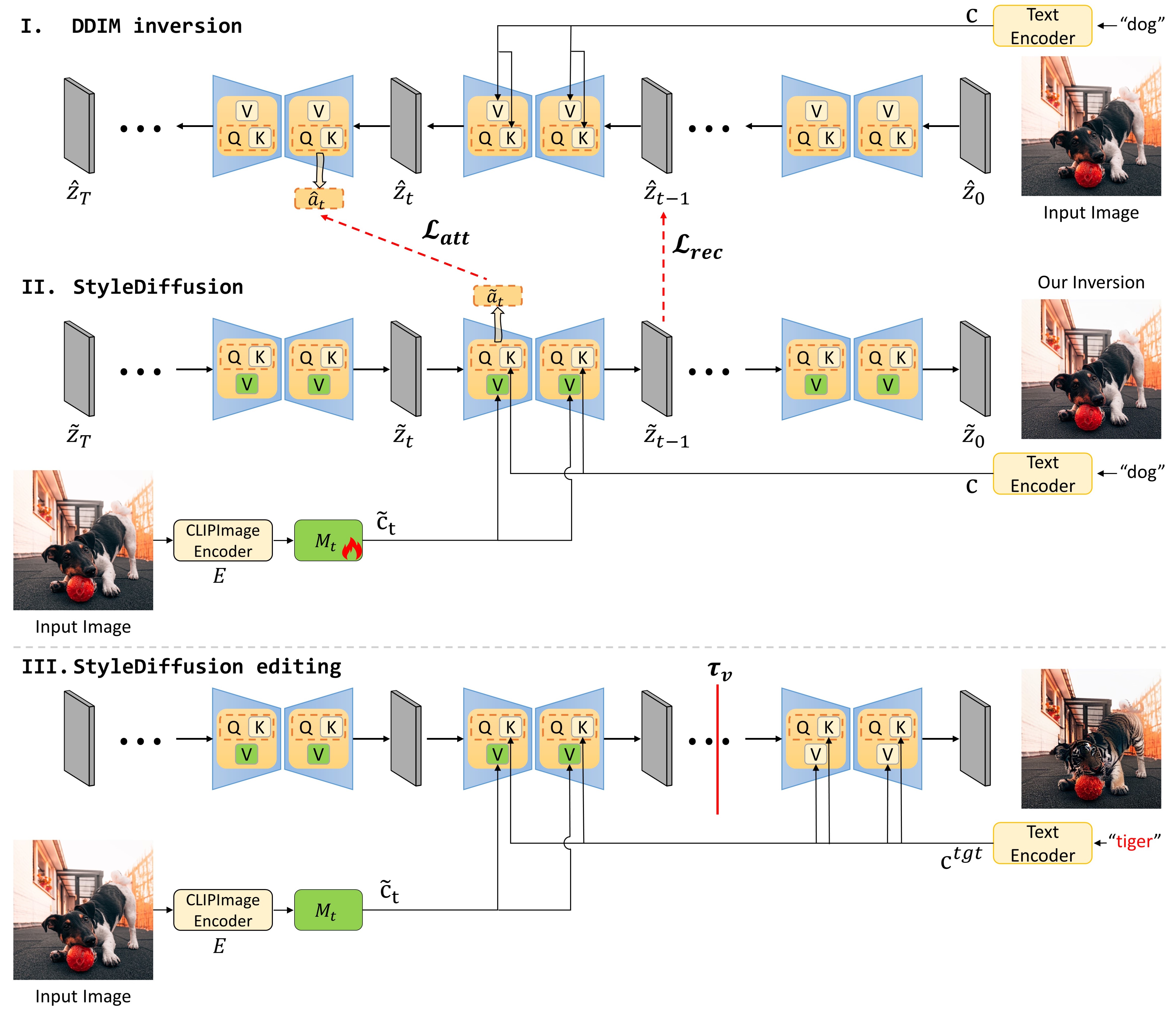
StyleDiffusion: Prompt-Embedding Inversion for Text-Based Editing
Senmao Li, Joost van de Weijer, Taihang Hu, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Qibin Hou, Yaxing Wang*, Jian Yang
- Only optimizing the input of the value linear network in the cross-attention layers is sufficiently powerful to reconstruct a real image
- Attention regularization to preserve the object-like attention maps after reconstruction and editing, enabling us to obtain accurate style editing without invoking significant structural changes
[paper]|
[中译版]
[code]
[abstract]
A significant research effort is focused on exploiting the amazing capacities of pretrained diffusion models for the editing of images. They either finetune the model, or invert the image in the latent space of the pretrained model. However, they suffer from two problems: (1) Unsatisfying results for selected regions, and unexpected changes in nonselected regions. (2) They require careful text prompt editing where the prompt should include all visual objects in the input image. To address this, we propose two improvements: (1) Only optimizing the input of the value linear network in the cross-attention layers, is sufficiently powerful to reconstruct a real image. (2) We propose attention regularization to preserve the object-like attention maps after editing, enabling us to obtain accurate style editing without invoking significant structural changes. We further improve the editing technique which is used for the unconditional branch of classifier-free guidance, as well as the conditional one as used by P2P. Extensive experimental prompt-editing results on a variety of images, demonstrate qualitatively and quantitatively that our method has superior editing capabilities than existing and concurrent works.
[中文解读]
CVPR 2023
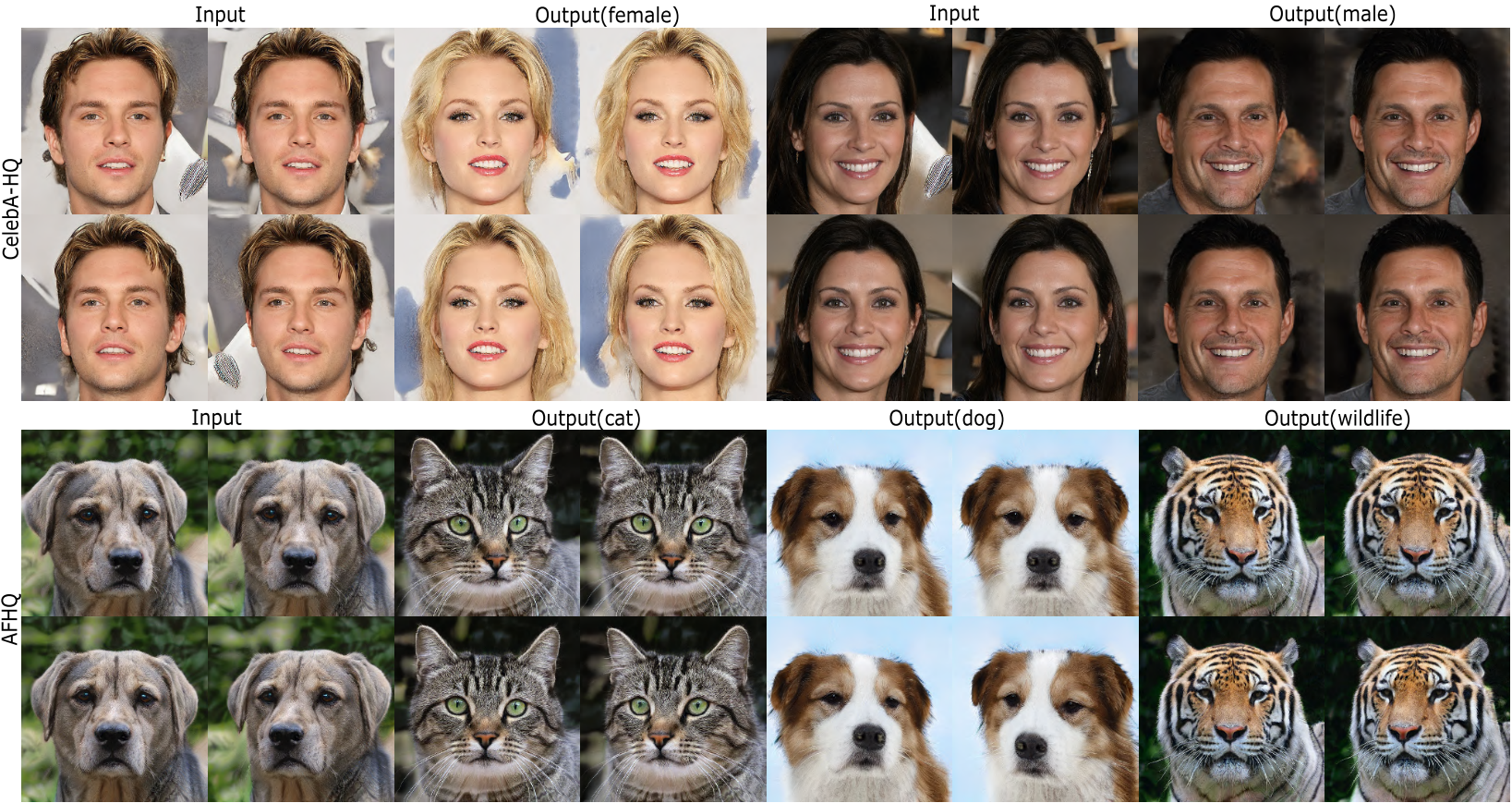

3D-Aware Multi-Class Image-to-Image Translation with NeRFs
Senmao Li, Joost van de Weijer, Yaxing Wang*, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Meiqin Liu, Jian Yang
- The first to explore 3D-aware multi-class I2I translation
- Decouple 3D-aware I2I translation into two steps
[paper]|
[中译版]
[code]
[abstract]
Recent advances in 3D-aware generative models (3D-aware GANs) combined with Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have achieved impressive results for novel view synthesis. However no prior works investigate 3D-aware GANs for 3D consistent multi-class image-to-image (3D-aware I2I) translation. Naively using 2D-I2I translation methods suffers from unrealistic shape/identity change. To perform 3D-aware multi-class I2I translation, we decouple this learning process into a multi-class 3D-aware GAN step and a 3D-aware I2I translation step. In the first step, we propose two novel techniques: a new conditional architecture and a effective training strategy. In the second step, based on the well-trained multi-class 3D-aware GAN architecture that preserves view-consistency, we construct a 3D-aware I2I translation system. To further reduce the view-consistency problems, we propose several new techniques, including a U-net-like adaptor network design, a hierarchical representation constrain and a relative regularization loss. In extensive experiments on two datasets, quantitative and qualitative results demonstrate that we successfully perform 3D-aware I2I translation with multi-view consistency.
[slide]
[poster]
-
 InterLCM: Low-Quality Images as Intermediate States of Latent Consistency Models for Effective Blind Face Restoration . Senmao Li, Kai Wang, Joost van de Weijier, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Chun-Le Guo, Shiqi Yang, Yaxing Wang, Jian Yang, Ming-Ming Cheng. ICLR2025.
InterLCM: Low-Quality Images as Intermediate States of Latent Consistency Models for Effective Blind Face Restoration . Senmao Li, Kai Wang, Joost van de Weijier, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Chun-Le Guo, Shiqi Yang, Yaxing Wang, Jian Yang, Ming-Ming Cheng. ICLR2025.
[paper]
[Project Page]
[abstract]
Diffusion priors have been used for blind face restoration (BFR) by fine-tuning diffusion models (DMs) on restoration datasets to recover low-quality images. However, the naive application of DMs presents several key limitations.
(i) The diffusion prior has inferior semantic consistency (e.g., ID, structure and color.), increasing the difficulty of optimizing the BFR model;
(ii) reliance on hundreds of denoising iterations, preventing the effective cooperation with perceptual losses, which is crucial for faithful restoration.
Observing that the latent consistency model (LCM) learns consistency noise-to-data mappings on the ODE-trajectory and therefore shows more semantic consistency in the subject identity, structural information and color preservation,
we propose InterLCM to leverage the LCM for its superior semantic consistency and efficiency to counter the above issues.
Treating low-quality images as the intermediate state of LCM, InterLCM achieves a balance between fidelity and quality by starting from earlier LCM steps.
LCM also allows the integration of perceptual loss during training, leading to improved restoration quality, particularly in real-world scenarios.
To mitigate structural and semantic uncertainties, InterLCM incorporates a Visual Module to extract visual features and a Spatial Encoder to capture spatial details, enhancing the fidelity of restored images.
Extensive experiments demonstrate that InterLCM outperforms existing approaches in both synthetic and real-world datasets while also achieving faster inference speed.
-
 Faster Diffusion: Rethinking the Role of the Encoder for Diffusion Model Inference . Senmao Li, Taihang Hu, Joost van de Weijier, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Linxuan Li, Shiqi Yang, Yaxing Wang, Ming-Ming Cheng, Jian Yang. NeurIPS2024.
Faster Diffusion: Rethinking the Role of the Encoder for Diffusion Model Inference . Senmao Li, Taihang Hu, Joost van de Weijier, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Linxuan Li, Shiqi Yang, Yaxing Wang, Ming-Ming Cheng, Jian Yang. NeurIPS2024.
[paper]
[Project Page]
[abstract]
One of the key components within diffusion models is the UNet for noise prediction. While several works have explored basic properties of the UNet decoder, its encoder largely remains unexplored. In this work, we conduct the first comprehensive study of the UNet encoder. We empirically analyze the encoder features and provide insights to important questions regarding their changes at the inference process. In particular, we find that encoder features change gently, whereas the decoder features exhibit substantial variations across different time-steps. This finding inspired us to omit the encoder at certain adjacent time-steps and reuse cyclically the encoder features in the previous time-steps for the decoder. Further based on this observation, we introduce a simple yet effective encoder propagation scheme to accelerate the diffusion sampling for a diverse set of tasks. By benefiting from our propagation scheme, we are able to perform in parallel the decoder at certain adjacent time-steps. Additionally, we introduce a prior noise injection method to improve the texture details in the generated image. Besides the standard text-to-image task, we also validate our approach on other tasks: text-to-video, personalized generation and reference-guided generation. Without utilizing any knowledge distillation technique, our approach accelerates both the Stable Diffusion (SD) and the DeepFloyd-IF models sampling by 41% and 24% respectively, while maintaining high-quality generation performance.
-
 Get What You Want, Not What You Don't: Image Content Suppression for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models . Senmao Li, Joost van de Weijer, Taihang Hu, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Qibin Hou, Yaxing Wang, Jian Yang. ICLR 2024.
Get What You Want, Not What You Don't: Image Content Suppression for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models . Senmao Li, Joost van de Weijer, Taihang Hu, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Qibin Hou, Yaxing Wang, Jian Yang. ICLR 2024.
[paper]
[code]
[abstract]
The success of recent text-to-image diffusion models is largely due to their capacity to be guided by a complex text prompt, which enables users to precisely describe the desired content. However, these models struggle to effectively suppress the generation of undesired content, which is explicitly requested to be omitted from the generated image in the prompt. In this paper, we analyze how to manipulate the text embeddings and remove unwanted content from them. We introduce two approaches, which we refer to as **soft-weighted regularization** and **inference-time text embedding optimization**. The first regularizes the text embedding matrix and effectively suppresses the undesired content. The second method aims to further suppress the unwanted content generation of the prompt, and encourages the generation of desired content. We evaluate our method quantitatively and qualitatively on extensive experiments, validating its effectiveness. Furthermore, our method is generalizability to both the pixel-space diffusion models (i.e. DeepFloyd-IF) and the latent-space diffusion models (i.e. Stable Diffusion).
-
 StyleDiffusion: Prompt-Embedding Inversion for Text-Based Editing . Senmao Li, Joost van de Weijer, Taihang Hu, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Qibin Hou, Yaxing Wang, Jian Yang. CVMJ 2024.
StyleDiffusion: Prompt-Embedding Inversion for Text-Based Editing . Senmao Li, Joost van de Weijer, Taihang Hu, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Qibin Hou, Yaxing Wang, Jian Yang. CVMJ 2024.
[paper]
[code]
[abstract]
A significant research effort is focused on exploiting the amazing capacities of pretrained diffusion models for the editing of images. They either finetune the model, or invert the image in the latent space of the pretrained model. However, they suffer from two problems: (1) Unsatisfying results for selected regions, and unexpected changes in nonselected regions. (2) They require careful text prompt editing where the prompt should include all visual objects in the input image. To address this, we propose two improvements: (1) Only optimizing the input of the value linear network in the cross-attention layers, is sufficiently powerful to reconstruct a real image. (2) We propose attention regularization to preserve the object-like attention maps after editing, enabling us to obtain accurate style editing without invoking significant structural changes. We further improve the editing technique which is used for the unconditional branch of classifier-free guidance, as well as the conditional one as used by P2P. Extensive experimental prompt-editing results on a variety of images, demonstrate qualitatively and quantitatively that our method has superior editing capabilities than existing and concurrent works.
-
 3D-Aware Multi-Class Image-to-Image Translation with NeRFs . Senmao Li, Joost van de Weijer, Yaxing Wang, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Meiqin Liu, Jian Yang. CVPR 2023.
3D-Aware Multi-Class Image-to-Image Translation with NeRFs . Senmao Li, Joost van de Weijer, Yaxing Wang, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Meiqin Liu, Jian Yang. CVPR 2023.
[paper]
[code]
[abstract]
Recent advances in 3D-aware generative models (3D-aware GANs) combined with Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have achieved impressive results for novel view synthesis. However no prior works investigate 3D-aware GANs for 3D consistent multi-class image-to-image (3D-aware I2I) translation. Naively using 2D-I2I translation methods suffers from unrealistic shape/identity change. To perform 3D-aware multi-class I2I translation, we decouple this learning process into a multi-class 3D-aware GAN step and a 3D-aware I2I translation step. In the first step, we propose two novel techniques: a new conditional architecture and a effective training strategy. In the second step, based on the well-trained multi-class 3D-aware GAN architecture that preserves view-consistency, we construct a 3D-aware I2I translation system. To further reduce the view-consistency problems, we propose several new techniques, including a U-net-like adaptor network design, a hierarchical representation constrain and a relative regularization loss. In extensive experiments on two datasets, quantitative and qualitative results demonstrate that we successfully perform 3D-aware I2I translation with multi-view consistency.
📄 Academic Service
💻 Internships






InterLCM: Low-Quality Images as Intermediate States of Latent Consistency Models for Effective Blind Face Restoration . Senmao Li, Kai Wang, Joost van de Weijier, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Chun-Le Guo, Shiqi Yang, Yaxing Wang, Jian Yang, Ming-Ming Cheng. ICLR2025.
Faster Diffusion: Rethinking the Role of the Encoder for Diffusion Model Inference . Senmao Li, Taihang Hu, Joost van de Weijier, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Linxuan Li, Shiqi Yang, Yaxing Wang, Ming-Ming Cheng, Jian Yang. NeurIPS2024.
Get What You Want, Not What You Don't: Image Content Suppression for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models . Senmao Li, Joost van de Weijer, Taihang Hu, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Qibin Hou, Yaxing Wang, Jian Yang. ICLR 2024.
StyleDiffusion: Prompt-Embedding Inversion for Text-Based Editing . Senmao Li, Joost van de Weijer, Taihang Hu, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Qibin Hou, Yaxing Wang, Jian Yang. CVMJ 2024.
3D-Aware Multi-Class Image-to-Image Translation with NeRFs . Senmao Li, Joost van de Weijer, Yaxing Wang, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Meiqin Liu, Jian Yang. CVPR 2023.
